3. Games in classroom
Learning Objectives
- The Learning Principles of EVG
- What we can learn with EVG?
- Why implementing EVG is important?
Positive impacts of gaming for students

We have researching and discovering how much games and video games have a positive impact both in life and in education.
- Motivational impact - encourages an incremental approach
- Cognitive - improves attention, focus, and reaction time
- Social - translates the social skills learned into relations outside the gaming environment
- Emotional - encourages positive mood states and adaptive emotion regulation
21st Century Skills
Students are prepared for the "globalized job market" because technology, effective instruction and authentic problems are combined so students learn collaboration, "critical-thinking", "communication skills" through the vehicle of DGBL.
What games provide
Games bring together combination of motivating elements not found together in any other medium. Here we can see some games virtues and the positive consequence:
- Games are a form of fun -> enjoyment and pleasure
- Games are a form of play -> intense and passionate engagement
- Games are rules -> structure, limits, prohibited behaviour
- Games are goals -> motivation to keep going on
- Games are interactive -> doing, the player has to do something
- Games are adaptive -> flow, keeps the mind focused, excited and not bored.
- Games have outcomes and feedback -> learning by errors
- Games have a win state -> ego gratification
- Games have conflict/competition/challenge/opposition -> adrenaline
- Games have problem solving -> sparks creativity
- Games have peer interaction -> social groups and communication
- Games have characters and story -> emotions and empathy
Learning Flow
Educational Games a special "flow", which is

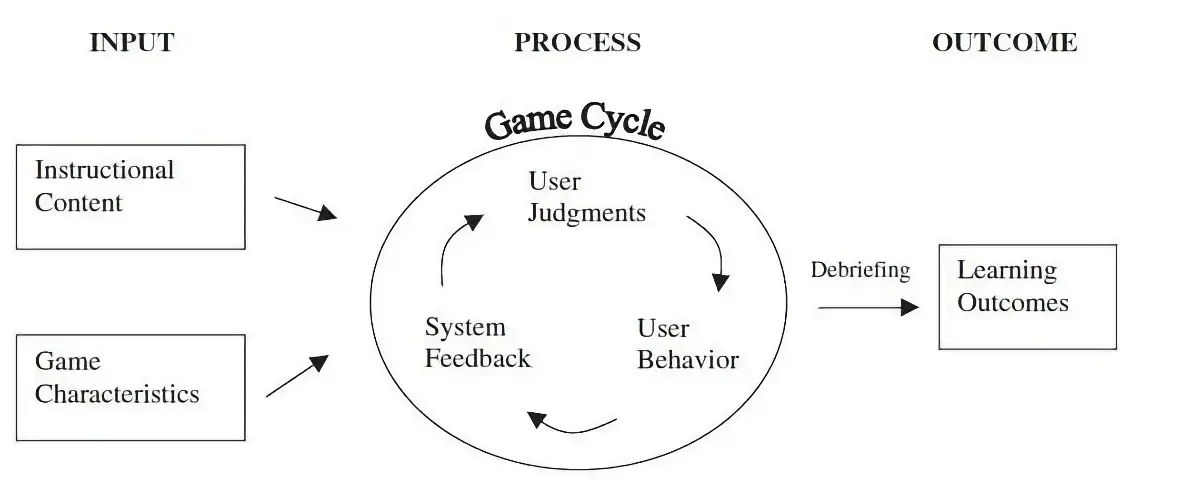
Video Games and new teaching methods
Recent studies have shown that introducing educational video games (EVG) and adopting a game-based learning teaching approach, has helped students achieve better learning performance, improved student engagement, promote motivation and active processing of educational content.
Introducing video games into the classroom enhances many learning and teaching skills that can help elevate the educational experience of the classroom. This teaching method uses beneficial aspects of video games to transmit knowledge to students. It is based on three key factors:
- It breathes life into education: it transforms learning into an enjoyable, thrilling game without boring lessons. Students assimilate and retain information almost without noticing.
- It boosts motivation: students are the main characters in the story and their success is rewarded with medals, extra lives, bonuses, etc. This captures and keeps their interest in learning.
- It gives opportunities to practice students can apply the knowledge they acquire without getting into dangerous situations. This is what flight and navigation simulators, for instance, are all about.
How effective are video games in the classroom?
 Let's see some Pros and Cons of video games
Let's see some Pros and Cons of video games
Pros
- Improve Tech Literacy
- Develop Multi-tasking mentality
- Experience Teamwork
- Practice Long-range planning
- Provide Individualised instruction
Cons
- Cost (higher than book-paper-pencil paradigm)
- Distraction from other objectives
- Social isolation
- Shortened attention span
- student competitiveness has been proven to get in the way of learning because students are more focused on winning the game instead of learning new skills.
- The design of games that achieve a balance between learning and fun continues to pose a challenge
- issues of unequal access and application
- requires well-educated and supported teachers
Learner Anxiety
The DGBL has shown to lower students' anxiety and increase their effective communication which could lead to improved processing of new information.
Let's see this video about why video games are such effective learning tools:
Video Learning through "serious games"
📽 VIDEO Video Learning through "serious games"
Cognitive skills and games
Cognitive processes let you: 1. Understand sensory inputs 2. Elaborate information 3. Remember and recall information 4. Contextualise information and solve problems
Here is a list of cognitive skills that can be developed by playing Video Games, or a Video Game can be designed to develop a particular set of skills.
Attention
Focused Attention
The ability to focus attention on a single stimulus
Divided Attention
The ability to execute more than one action at a time, while paying attention to a few channels of information.
Inhibition
The ability to ignore irrelevant stimuli or suppress irrelevant reactions while performing a task.
Updating
The ability to respond in a flexible and adaptive manner in order to keep up with the changes in the environment.
Memory
Short-Term Memory
The ability to hold a small amount of information in a readily, available state for a short period of time.
Naming
The ability to retrieve a word from our semantic lexicon and is considered to be a basic ability.
Working Memory
Refers to the temporary storage and manipulation of the information necessary for complex cognitive tasks.
Contextual Memory
The conscious recall of the source and circumstances of a specific memory.
Visual Short-Term Memory
The ability to temporarily retain a small amount of visual information.
Non-verbal Memory
The ability to store and retrieve information which are non-verbal by nature.
Phonological Short-term Memory
The ability to remember phonological information over a brief period of time.
Sensation and Perception
Auditory perception
Auditory Perception is the ability to perceive and understand the difference between sounds.
Visual Perception
The ability to interpret information from the effects of visible light reaching the eye.
Spatial Perception
The ability to evaluate how things are arranged in space, and investigate their relations in the environment.
Visual Scanning
The ability to actively find relevant information in our surroundings quickly and efficiently.
Estimation
The ability to estimate an object's future location based on its current speed and distance.
Width of Field of View
Corresponds to amount of information we receive from around when looking straight ahead.
Recognition
The ability to retrieve information from the past and to recognise certain events, places or other information.
Reasoning and Comprehension
Processing Speed
Involves the ability to fluently perform easy or over-learned tasks.
Planning
The ability to "think ahead", to mentally anticipate the correct way to execute a task.
Shifting
Ability to adapt behaviour and thoughts to new, changing, or unexpected circumstances
Coordination
Hand-eye Coordination
The level of sensitivity with which the hand and eye are synchronised.
Response Time
The ability to perceive and process a simple stimulus and respond to it.
Learning Principles
Here are the 16 principles of good video-game based learning:
- Identity: Players build a sense of identity throughout the video game, either through direct input or an on-screen character they inherit.
- Interaction: Communication occurs between the player and the game.
- Production: Gamers help produce the story through some form of interaction, such as choosing a path, solving a puzzle or completing a level.
- Risk Taking: Failing in a game holds few consequences in comparison to real life, empowering players to take risks.
- Customized: Games usually offer a level of customization so that users can play - and succeed - at their competency level.
- Agency: Players have control over the gaming environment.
- Well-Ordered Problems: The gaming environment contains problems that naturally lead into one another, allowing a player’s mastery to grow and evolve.
- Challenge and Consideration: Games offer a problem that challenges students’ assumed expertise.
- Just in Time or On Demand: Players receive information as they need it, not before, which teaches them patience and perseverance and improves critical-thinking abilities.
- Situated Meanings: Students learn new vocabulary words by experiencing them within game situations.
- Pleasantly Frustrating: The game should frustrate the student enough to challenge them but be easy enough that they believe and can overcome the problem(s) faced.
- System Thinking: Games make players think in a bigger picture, not just individual actions taken, helping them see how the pieces fit or can be fitted together.
- Explore, Think Laterally, Rethink Goals: Games force players to expand their situational knowledge and consider courses of action other than linear ones.
- Smart Tools and Distributed Knowledge: In-game tools help students understand the world. Through using them, they gain confidence to share their knowledge with others.
- Cross-Functional Teams: In multiplayer environments, players have different skills, forcing them to rely on each other - a needed soft skill for students.
- Performance before Competence: Competency occurs through taking action in the game, reversing the typical model in which students are required to learn before being allowed to act.
These learning principles should be applied to school learning at all times, not just through educational video games. They change the current trend for skill-and-drill, scripted instruction, and standardized multiple-choice testing.
What we can learn with EVG
Today we can find videogames that can help in every learning field.
For example: - Language Learning / Literacy - Mathematics and Science (STEM) - Social Studies and History - Development of Cognitive Skills - Rehabilitation - Music - Art / Creative skills - Emotional Health / Wellbeing - Ethics and Ethical Thinking - Management
In the Case Studies chapter we'll see some examples.
When and why implement EVGs?
You must remember that game-based learning and EVGs are tools that should supplement/facilitate your pedagogy, they are not the teacher. When using these techniques in your classroom, do not grade play, instead assess the learning transfer that has been facilitated from the game experience to the curriculum.
Therefore, choosing to implement EVGs should come as a reason to enhance content delivery and comprehension as well as motivate students to understand complex theories/content in a mind engaging and challenging manner.
16 reasons as to why to implement EVGs in the classroom
- Promote technology exploration
- Develop problem-solving skills
- Develop educational mastery and complete tasks in a logical manner
- Develop reasoning and complexity thinking
- Develop fine motor skills
- Build interest in STEAM fields
- Teach Students basic programming
- Develop confidence and social skills
- Learn Collaboration skills
- Emphasize also individualized learning
- Provide a safe environment to explore and in which to make mistakes
- Learn through enjoyment and "fun"
- Contextualised, goal oriented instead of abstract learning
- Experiential learning: learning by doing
- Intrinsic motivation: playing is voluntary and self-driven
- Seamless accountability and feedback
📽 #VIDEO What can schools learn from video games?
Unit review
Discuss, in your opinion the importance of implementing game-based learning. Could there be complications to this process? if so, what would they be?